Spring Boot Demo Project
Take a look at a Spring Boot-based REST API leveraging Result objects
Generating the Project
Adding Serialization Support
dependencies {
// ...
implementation platform('com.leakyabstractions:result-bom:1.0.0.0')
implementation 'com.leakyabstractions:result'
implementation 'com.leakyabstractions:result-jackson'
}@Configuration
public class JacksonConfig {
@Bean
public Module registerResultModule() {
return new ResultModule();
}
}API Responses
Controllers
Running the Application
Testing the Server
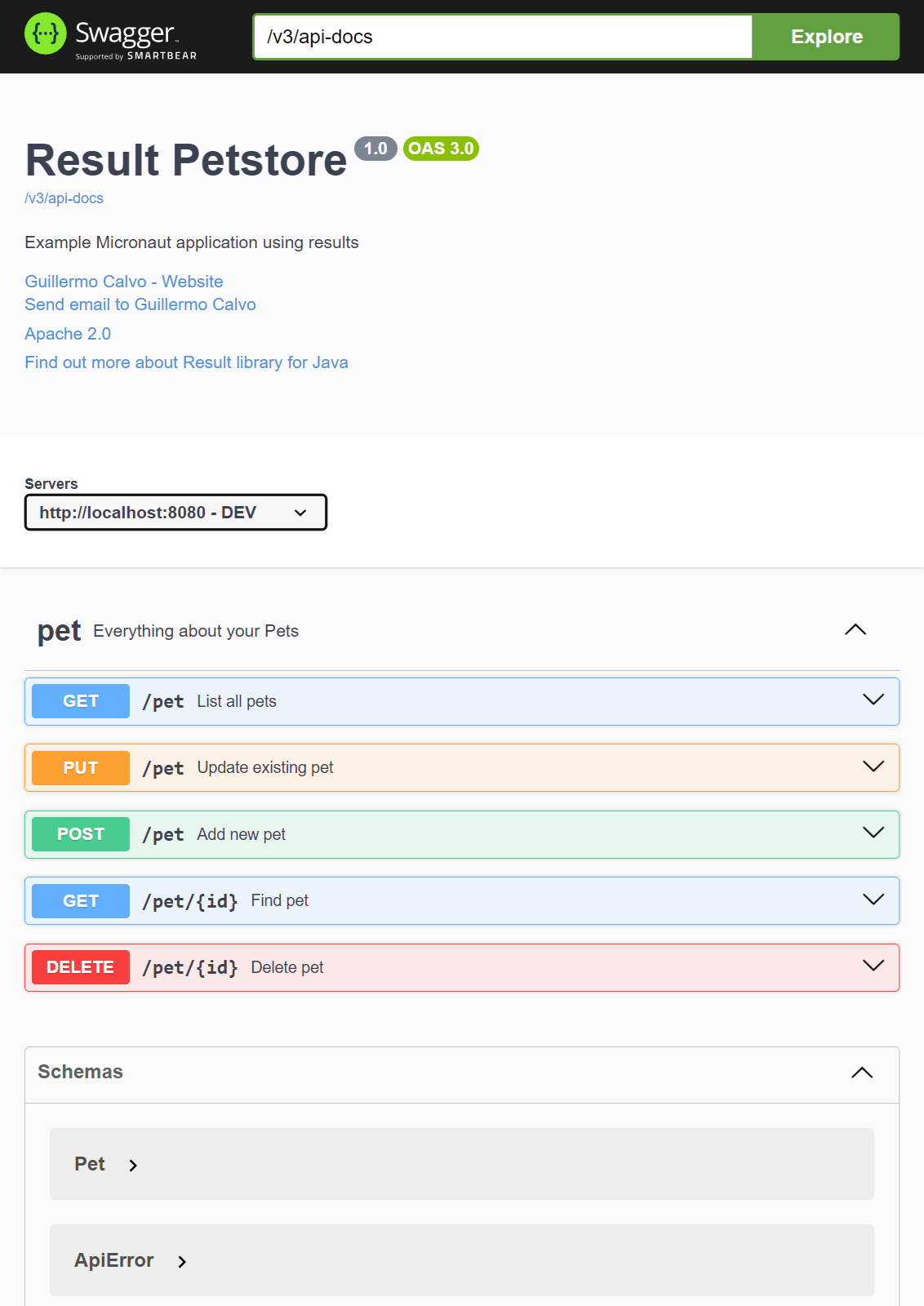
Using Swagger-UI
Last updated
Was this helpful?